Discover the Dark Side of Decentralization no one talks about—hidden risks, governance failures, security flaws, and real-world consequences behind the Web3 promise.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Decentralization is often portrayed as the ultimate solution to everything wrong with traditional systems. From finance to governance, from data ownership to digital identity, decentralization promises freedom, transparency, and trust without intermediaries. But what if this promise has a side most people conveniently ignore?
While decentralization removes central control, it does not automatically remove risk, power imbalance, or manipulation. In fact, in some cases, it introduces entirely new problems that are harder to detect and even harder to fix.
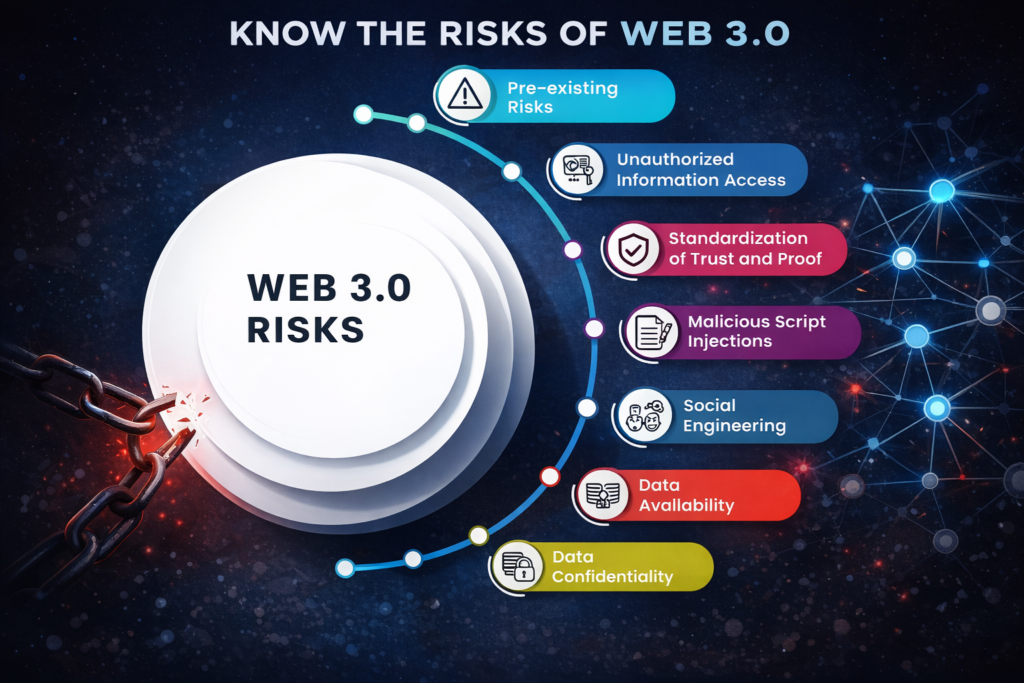
This article explores the Dark Side of Decentralization—the uncomfortable realities that rarely appear in marketing decks, conference talks, or influencer threads. Understanding these risks is essential for investors, builders, and users who want to participate in Web3 responsibly.
The Ideal Vision vs. the Real World
In theory, decentralization means:
- No single point of failure
- Equal participation
- Transparent rules
- Trustless systems
In practice, many decentralized platforms quietly drift toward informal centralization, where power concentrates in the hands of a few—developers, validators, whales, or governance insiders.
This gap between theory and reality is where the Dark Side of Decentralization begins.
Hidden Centralization Behind “Decentralized” Labels
One of the least discussed issues is how many decentralized systems are only decentralized on paper.
Examples include:
- A small group controlling governance votes
- Core developers having upgrade authority
- Infrastructure hosted on centralized cloud services
Even widely used DeFi and DAO platforms rely heavily on centralized components like RPC providers or front-end servers.
You can explore real-world examples and critical reporting on decentralization failures through platforms like CoinDesk and The Block.
Governance Without Accountability
Decentralized governance sounds democratic—until something goes wrong.
In traditional systems, accountability is clear. In decentralized systems:
- Who is responsible for bugs?
- Who compensates users after hacks?
- Who resolves disputes?
Often, the answer is: no one.
Token-based governance can also be manipulated by wealthy holders, turning “community governance” into a plutocracy. This governance vacuum is a major component of the Dark Side of Decentralization that many newcomers overlook.
Security Risks Are Not Always Visible
Decentralization removes centralized custody—but it shifts responsibility to users who may not be prepared for it.
Common risks include:
- Smart contract vulnerabilities
- Private key mismanagement
- Irreversible transactions
- Exploitable governance proposals
According to blockchain security reports frequently cited by Chainalysis, billions of dollars have been lost due to exploits—not because users were careless, but because systems were overly complex and poorly audited.
Decentralization does not eliminate trust; it replaces institutional trust with technical trust, which most users don’t fully understand.
The Illusion of Privacy
Many believe decentralization equals privacy. In reality, public blockchains are radically transparent.
Once an address is linked to an identity:
- Transaction history becomes permanent
- Financial behavior is exposed
- Surveillance becomes easier, not harder
Governments and corporations increasingly use on-chain analytics tools to track activity. This creates a paradox where decentralization enhances traceability instead of privacy—another overlooked aspect of the Dark Side of Decentralization.
Regulatory Blind Spots and Legal Chaos
Decentralized systems often operate in legal gray areas.
Problems include:
- No legal entity to regulate
- Unclear jurisdiction
- Conflicting international laws
When regulators intervene, users—not protocols—often pay the price through frozen assets, blocked access, or compliance crackdowns.
For broader regulatory perspectives, readers can refer to policy analysis published by organizations like World Economic Forum.
Environmental and Infrastructure Costs
While newer blockchains are more energy-efficient, decentralization still carries infrastructure costs:
- Validator hardware
- Network bandwidth
- Redundant storage
Some networks sacrifice decentralization to improve scalability, while others sacrifice efficiency to preserve ideological purity. These trade-offs are rarely discussed honestly in mainstream Web3 narratives.
User Experience: Freedom Comes With Friction
Decentralized platforms often prioritize ideology over usability.
Challenges include:
- Complex wallets
- Confusing interfaces
- No customer support
- Permanent mistakes
For mass adoption, decentralization must compete with the simplicity of centralized platforms. Until then, the Dark Side of Decentralization will continue to push everyday users back toward custodial solutions.
Economic Inequality Inside Decentralized Systems
Ironically, decentralization can amplify inequality.
Early adopters often:
- Accumulate large token holdings
- Control governance outcomes
- Shape protocol direction
Late users participate in systems where power is already unevenly distributed. This mirrors traditional financial inequality—just under a different label.
Is Decentralization Still Worth It?
Despite its flaws, decentralization remains a powerful idea. The problem is not decentralization itself—but blind faith in it.
Decentralization works best when:
- Combined with strong security practices
- Balanced with clear accountability
- Designed for real users, not just ideology
Understanding the Dark Side of Decentralization doesn’t mean rejecting Web3—it means engaging with it intelligently.
Final Thoughts
Decentralization is not a magic cure. It is a tool—powerful, transformative, but imperfect.
Ignoring its downsides leads to:
- Poor investment decisions
- Weak governance systems
- Loss of trust
By openly discussing the Dark Side of Decentralization, the Web3 ecosystem can mature beyond hype and move toward sustainable innovation.
True decentralization is not about removing all control—it’s about designing systems where power is transparent, limited, and accountable.
Stuck between the hustle and the yield? We break down passive income vs active trading to reveal which strategy scales your wealth and frees your time in 2026.